Search Results
Results for: 'Glycogen anabolism'
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 6996
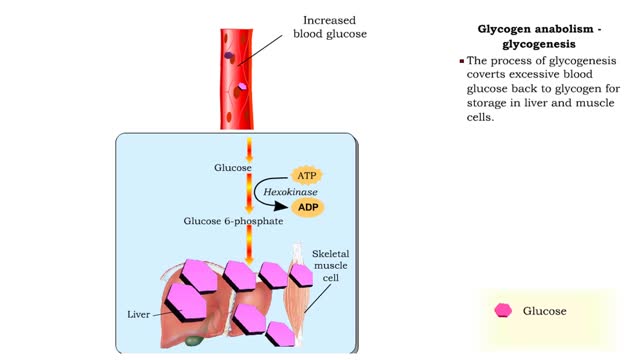
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 6409
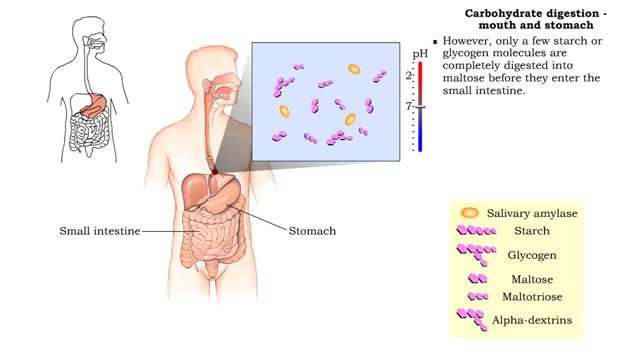
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 7028
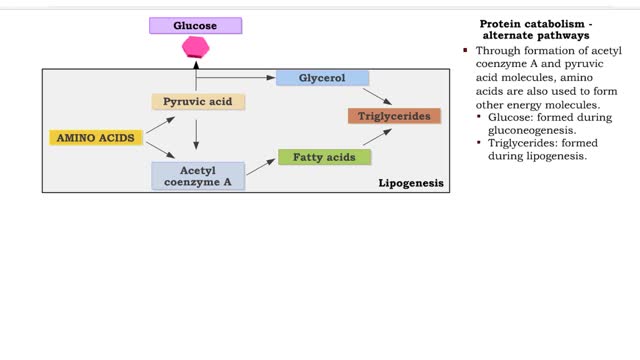
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
By: HWC, Views: 6815
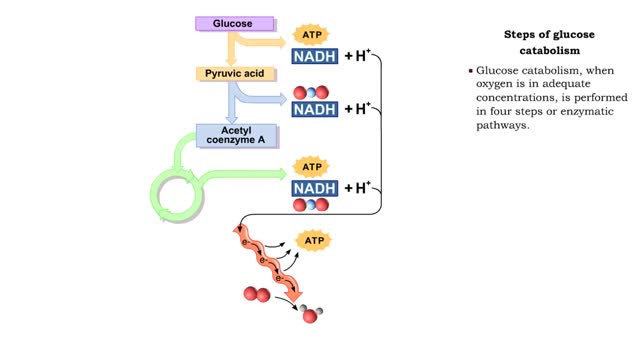
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
By: HWC, Views: 843
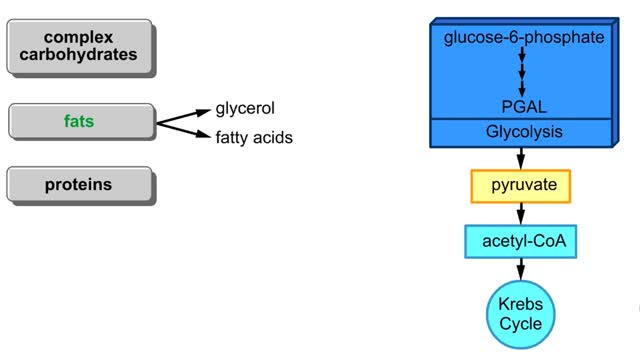
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 7193
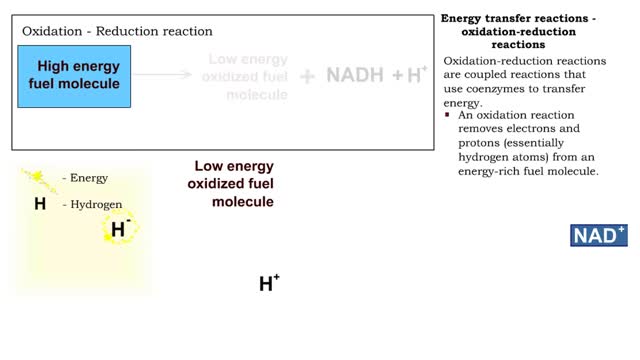
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 6984
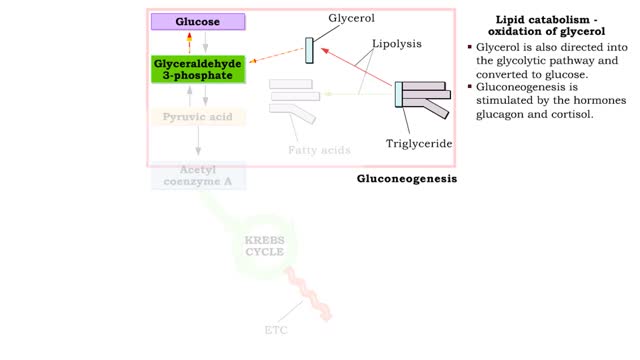
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 6785
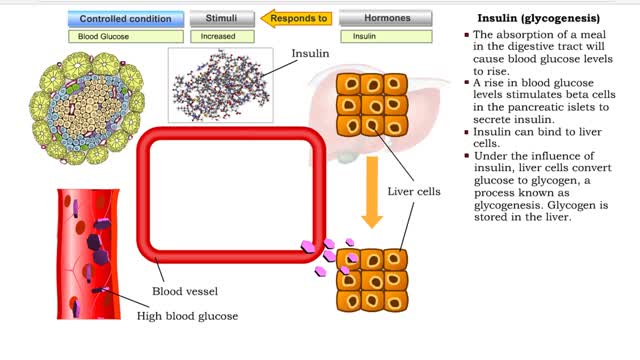
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 6206
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
Advertisement